
Why a Structured Framework for Growth Hacking Matters
Framework growth hacking is a systematic, data-driven approach to achieving rapid business growth. Unlike random “growth hacks,” a proper framework provides repeatable processes to identify opportunities, prioritize experiments, measure results, and scale what works—turning one-off wins into sustainable growth engines. It relies on key components like the AARRR funnel, the G.R.O.W.S. experimentation process, prioritization models (ICE/RICE), a North Star Metric, and a cross-functional team.
The confusion around growth hacking stems from a misunderstanding. It’s not about clever tricks. The real power lies in having clear processes that enable you to quickly test ideas and compound small wins. Companies like Dropbox, Airbnb, and LinkedIn didn’t find magic bullets; they built systematic approaches to growth.
Without a structured framework, businesses often chase random tactics, waste resources, and fail to learn from experiments. This leads to inconsistent results and frustrated teams.
I’m Chris Hornak, Co-Founder of Swift Growth Marketing. We’ve used these principles to help clients achieve results like 764% traffic increases through systematic experimentation. Sustainable growth comes from building a disciplined process that turns your organization into a learning machine.
What is Growth Hacking?
Growth hacking is a dynamic approach focused on rapid experimentation to find the most effective ways to grow a business. Coined by Sean Ellis in 2010, it’s a mindset for achieving exponential growth with limited resources. It’s about being relentlessly curious and analytical to exploit opportunities for user acquisition, activation, retention, and revenue.
How does this differ from traditional marketing? Traditional marketing often operates with larger, fixed budgets and longer campaigns, focusing on broad brand awareness. Growth hacking is characterized by its continuous, iterative experimentation. Growth teams are cross-functional, bringing together skills from marketing, product, engineering, and data to solve growth challenges. The focus is always on rapid, scalable growth.
Here’s a quick overview of the key differences:
| Aspect | Growth Hacking | Traditional Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Rapid, scalable growth | Brand awareness, steady growth |
| Process | Iterative, experiment-driven | Planned, campaign-based |
| Budget | Lean, efficient | Larger, fixed |
| Team Structure | Cross-functional, agile | Specialized, siloed |
Core Principles of Growth Hacking
At its heart, growth hacking is built upon several foundational principles:
- Data-Driven Decisions: We don’t guess; we test and measure. Every hypothesis is informed by data, which offers insights into user behavior and campaign performance.
- Rapid Experimentation: Growth hacking is a cycle of building, measuring, and learning. We accept a “fail fast, learn faster” mentality, constantly running small experiments to find what works.
- Product-Led Thinking: Growth is deeply integrated with the product. We leverage product features and user experience to drive acquisition, activation, and retention.
- User-Centricity: We put the user at the center of everything. Understanding their needs and pain points allows us to craft solutions that add value.
- Creativity: While data-driven, growth hacking demands creative thinking to find innovative ways to reach audiences and optimize funnels.
- Agility and Adaptability: The digital landscape is always changing. We must be agile and ready to pivot based on new data. This requires a Growth Marketing Mindset that accepts change and continuous learning.
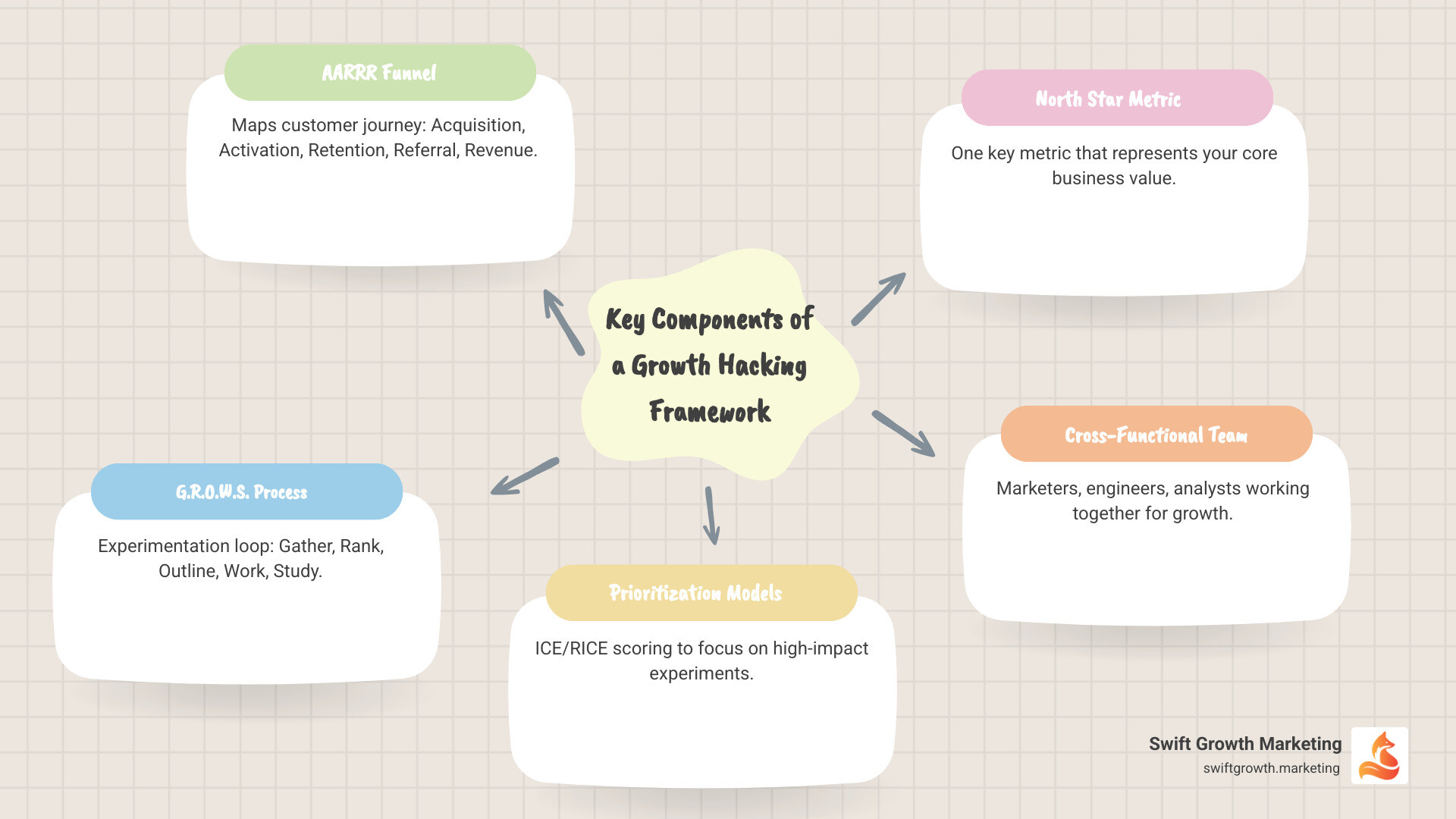
Core Models: Your Framework for Growth Hacking
To bring these principles to life, we rely on established models that provide structure to our growth efforts. These are practical tools we use daily to guide strategy and measure progress. Think of them as blueprints for our Growth Marketing Framework. Understanding these models is key to mastering the Key Elements of Growth Marketing and implementing a successful framework growth hacking strategy.
The AARRR “Pirate” Funnel: The Customer Journey Map
The AARRR funnel, or “Pirate Metrics,” was developed by Dave McClure and is a cornerstone of growth hacking. It provides a clear view of the customer journey, allowing us to identify bottlenecks and optimize each of the five key stages:
- Acquisition: How users find us (e.g., SEO, social media, paid ads). The goal is to drive qualified traffic.
- Activation: When users experience the product’s core value, their “aha!” moment. We aim to get users to this point as quickly as possible.
- Retention: How we keep users coming back. This is crucial as retaining customers is cheaper than acquiring new ones.
- Referral: How users become advocates and bring in new users. This is where viral loops and referral programs shine, like Dropbox’s famous referral program.
- Revenue: How we monetize users, involving pricing strategies, upselling, and cross-selling.
For each stage, we identify an OMTM (One Metric That Matters) to focus our efforts and measure true impact.
The G.R.O.W.S. Process: The Experimentation Loop
The G.R.O.W.S. process, developed by Growth Tribe, is a practical, 5-step loop for running growth experiments systematically. It’s our engine for continuous learning within the framework growth hacking approach.
- Gather Ideas (G): The brainstorming phase where we collect potential experiment ideas from all sources, like user feedback, data analysis, and team discussions.
- Rank Ideas (R): We prioritize ideas using frameworks like ICE or RICE, scoring them based on potential impact, confidence, and ease of implementation.
- Outline Experiment (O): We carefully plan each experiment, defining the hypothesis, target audience, duration, and success metrics. We aim for quick, simple experiments.
- Work (W): The execution phase where the team implements the experiment, such as setting up A/B tests or launching campaigns.
- Study Outcome (S): After the experiment, we analyze the results. We determine what we learned, even from a “failed” experiment, to gather actionable insights.
This process is iterative. Learnings from all experiments feed back into the “Gather Ideas” phase, restarting the loop. For a deeper dive, check out The G.R.O.W.S. process explained.
Prioritization Frameworks: ICE & RICE
When we have many ideas, we need a way to objectively decide which to pursue. Prioritization frameworks like ICE and RICE are crucial tools within our framework growth hacking toolkit.
The ICE framework, often credited to Sean Ellis, scores ideas on three factors:
- Impact: How much will this idea move our key metrics?
- Confidence: How sure are we that this idea will work?
- Ease: How difficult is it to implement this idea?
Each factor is scored (e.g., 1-10), and the scores are multiplied to prioritize ideas.
The RICE framework adds another dimension:
- Reach: How many people will this experiment affect?
- Impact: Same as ICE.
- Confidence: Same as ICE.
- Effort: The inverse of “Ease,” measuring the total resources required.
RICE is calculated as (Reach x Impact x Confidence) / Effort. This is useful for larger projects where reach is a critical consideration.
Both frameworks help us assess ideas in a structured way, making our decision-making process more robust.
The 4-Step Growth Hacking Process in Action
Our framework growth hacking approach is a continuous cycle that mirrors the scientific method: Ideation, Implementation, Experimentation, and Analysis. This ensures we’re always learning and optimizing. A crucial prerequisite is achieving product-market fit. As research highlights, if 40% or more of your users would be “very disappointed” without your product, you’ve likely reached this threshold. Without it, growth efforts are futile. Product-market fit is essential for growth.
Step 1: Ideation & Opportunity Identification
This is where we fill our experiment backlog with promising ideas. We use several techniques to uncover opportunities:
- Brainstorming: Our cross-functional team holds sessions to generate diverse ideas.
- User Feedback: We analyze support tickets, conduct surveys, and monitor social media to understand user pain points and desires.
- Data Analysis: We dive into analytics to find drops in our AARRR funnel, high churn rates, or underperforming channels that need attention.
- Competitor Analysis: We observe competitors’ strategies to find inspiration and identify gaps we can exploit.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Visualizing the user journey helps us identify friction points and opportunities for experimentation.
This step is about asking, “Where can we make the biggest impact with the least effort?” and helps us identify promising Growth Marketing Channels to explore.
Step 2: Proven Growth Hacking Strategies and Tactics
Once we’ve identified opportunities, we turn to a playbook of proven strategies. These are adaptable tools, not one-size-fits-all “hacks.”
- Referral Programs: We design programs that incentivize both the referrer and the referred, making sharing irresistible, like Dropbox’s famous program.
- Content Hacking: Creating valuable, shareable content that attracts customers through organic search and social media. For more detailed insights, explore SEO Growth Hacks.
- Product-Led Growth (PLG): Baking growth directly into the product, making it the primary driver of acquisition, activation, and retention.
- “Aha” Moment Optimization: Streamlining onboarding to ensure new users quickly experience the product’s core value.
- Gamification: Incorporating game-like elements (points, badges) to increase user engagement, as seen with Duolingo.
- Viral Loops: Creating self-perpetuating cycles where existing users bring in new ones, like Hotmail’s classic email footer.
We test these strategies rigorously to find the optimal mix for your business.
Step 3: Implementing Your Framework for Growth Hacking
This is where planning meets action. We design and execute experiments that are quick, measurable, and provide clear insights.
- Experiment Design: Each experiment starts with a clear hypothesis (e.g., “If we simplify our signup form, we believe conversions will increase by 15%”).
- A/B Testing: We use tools to split-test variations of a page, email, or feature to validate hypotheses without heavy developer work.
- Minimum Viable Test (MVT): We design lean experiments to validate ideas before significant investment, such as testing a value proposition with a landing page.
- Agile Marketing: We work in short sprints, allowing us to respond quickly to new data and market conditions.
- Setting Up Tracking: Before launch, we ensure robust tracking is in place to monitor our OMTM and key actions.
Integrating UX/UI designers and developers into the growth team allows us to swiftly implement and test product improvements. For insights on tools that facilitate this, see our guide on Tools for experimentation.
Step 4: Analysis, Learning, and Scaling
The final step is analyzing results, extracting learnings, and deciding what’s next.
- Data Analysis: We analyze both quantitative data (metrics, conversion rates) and qualitative data (user feedback, surveys).
- Statistical Significance: We ensure our results aren’t just random fluctuations before making decisions.
- Iteration: Not every experiment succeeds. We analyze why an experiment failed, refine our hypothesis, and design a new iteration. This continuous learning loop is key.
- Creating Playbooks: Successful experiments are documented and turned into repeatable “playbooks,” creating an invaluable knowledge base.
- Scaling Successful Experiments: When an experiment is a proven success, we scale it by rolling it out to all users or increasing the budget.
This rigorous cycle of testing, learning, and adapting is the engine of sustainable growth. For tips on maximizing your return, check out 5 Tips to Getting a Better ROI from Your Growth Marketing Budget.
Building a Growth Engine: Culture, Metrics, and Pitfalls
A robust framework growth hacking strategy is embedded in an organization’s culture and its approach to measurement. Building a true growth engine requires fostering a specific mindset, focusing on the right metrics, and avoiding common traps. This is especially true for Growth Marketing for Established Brands adapting to this agile approach.
Measuring Success with a North Star Metric
To know if we’re truly growing, we rally around a single North Star Metric (NSM). This is the one key metric that best represents the core value our product delivers to customers. It’s a leading indicator of success that predicts future growth.
For example:
- Patreon: Number of creators earning over a certain amount.
- Miro: Number of collaborative boards.
- Netflix: Median view hours per month.
The NSM aligns the entire company on what truly matters. Every team’s efforts should contribute to moving this metric. We also track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that feed into our NSM for more granular insights. For more examples, explore these Examples of North Star Metrics.
Building a Cross-Functional Growth Team
Growth hacking requires a dedicated, cross-functional team with diverse skills. As noted in “Hacking Growth,” breaking down traditional silos is key. Our ideal growth team includes:
- Growth Lead: The strategist who defines the NSM, oversees the growth strategy, and champions the growth mindset.
- Growth/Performance Marketer: The expert in acquisition and activation channels who designs and executes campaigns.
- Full-Stack Developer: Crucial for implementing experiments quickly and bridging the gap between ideas and technical feasibility.
- Data Analyst: The numbers wizard who sets up tracking, analyzes results, and ensures statistical significance.
- UX/UI Designer: The user advocate who optimizes user flows and ensures the product experience is intuitive.
This collaborative structure allows for rapid iteration. A Growth Marketing Agency for Startups can be an invaluable partner in building or augmenting such a team.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Your Framework for Growth Hacking
Even with the best framework, common traps can derail growth efforts. We’ve learned to spot and avoid these:
- Lack of Clear Goals: Without a defined NSM and specific KPIs, efforts become aimless.
- Fear of Failure: A culture that punishes failure stifles the innovation that comes from experimentation.
- Poor Documentation: Failing to document hypotheses, results, and learnings leads to repeated mistakes.
- Focusing Only on Acquisition: Neglecting activation, retention, and referral creates a leaky bucket.
- Not Achieving Product-Market Fit First: Trying to growth hack a product nobody wants is a waste of resources.
- Chasing “Hacks” Instead of Process: Sustainable growth comes from a systematic process, not from chasing the latest viral fad.
Frequently Asked Questions about Growth Hacking Frameworks
How is growth hacking different from traditional marketing?
Growth hacking differs from traditional marketing in its core objective and methodology. Traditional marketing often focuses on long-term brand building and awareness with planned campaigns and larger budgets. Growth hacking is hyper-focused on rapid, scalable growth through a data-driven, experimental process across the entire customer funnel. It uses cross-functional teams to find the most effective and often unconventional paths to growth.
What is the most important prerequisite for growth hacking?
The most critical prerequisite is product-market fit. This means you have a product that a significant market segment genuinely needs. Without it, growth efforts are futile, as you can attract users, but they won’t stay if the product doesn’t deliver value. The “Very Disappointed” method by Sean Ellis is a great way to gauge this; if fewer than 40% of your users would be very disappointed if your product disappeared, you likely haven’t reached this milestone.
Can B2B companies use growth hacking frameworks?
Absolutely. While tactics may differ from B2C, the underlying principles of data-driven experimentation and full-funnel optimization are universal. For B2B, growth hacking might involve experimenting with LinkedIn ads, account-based marketing (ABM), or optimizing onboarding for business accounts. The key is to adapt the framework to the unique B2B customer journey, always focusing on delivering measurable value.
Conclusion
We hope this guide has demystified framework growth hacking. It’s not about magic tricks but a disciplined, systematic process for achieving sustainable business growth. By embracing a data-driven mindset, leveraging frameworks like AARRR and G.R.O.W.S., and building cross-functional teams, you can turn your organization into a learning machine that consistently scales growth opportunities.
At Swift Growth Marketing, we’ve seen this approach transform companies in Pittsburgh, PA, and Wheeling, WV, driving significant increases in traffic and revenue.
Ready to stop guessing and start growing? Take the next step with our expert Growth Marketing Consultancy services. We’re here to partner with you on your journey to digital success.

